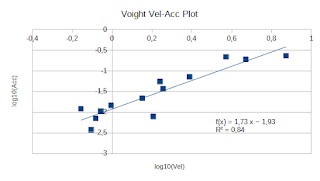
Leggendo alcuni articoli ho visto che viene consigliato l'utlilizzo di XGBoost al posto di LSTM sul forecasting di serie tempo...proviamoci con i dati gia' usati nei tentativi precedenti
Guardando il grafico si conferma che se il modello non conosce una accelerazione non e' in grado di prevederla anche se si usa variabile forzante come la pioggia
Inoltre non vedo particolari motivi per privilegiare XGBoost su LSTM
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""xgboost.ipynb
Automatically generated by Colab.
Original file is located at
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1zmFI2Djb4bD1hVbJfvFGYgqh0EpfRnRj
"""
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
dati = pd.read_csv('/content/prima.csv')
print(dati)
train = dati.head(int(len(dati)*0.8))
test = dati.tail(int(len(dati)*0.2))
train["Data"] = pd.to_datetime(train["Data"])
test["Data"] = pd.to_datetime(test["Data"])
train = train.set_index("Data")
test = test.set_index("Data")
train["Est"].plot( , figsize=(10, 5), label="train")
test["Est"].plot(style="b", figsize=(10, 5), label="test")
plt.title("Dati")
plt.legend()
X_train = train.drop('Est', axis =1)
y_train = train['Est']
X_test = test.drop('Est', axis =1)
y_test = test['Est']
!pip install xgboost
import xgboost as xgb
reg = xgb.XGBRegressor(n_estimators=1000)
reg.fit(X_train, y_train, verbose = False)
xgb.plot_importance(reg)
test['Est_Prediction'] = reg.predict(X_test)
train['Est'].plot(style='k', figsize=(10,5), label = 'train')
test['Est'].plot(style='b', figsize=(10,5), label = 'test')
test['Est_Prediction'].plot(style='r', figsize=(10,5), label = 'prediction')
plt.title('XGBoost')
plt.legend()